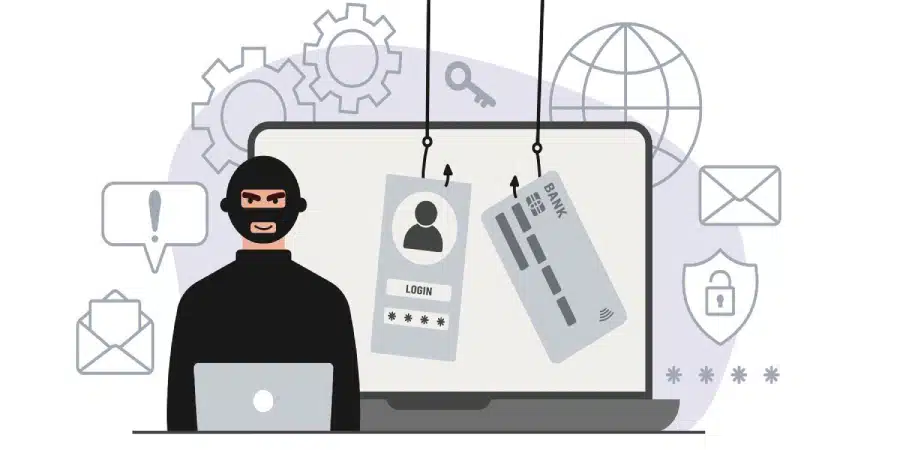
Account takeover fraud (ATO) presents a growing challenge for financial institutions (FIs) worldwide, jeopardizing both the financial security of institutions and the peace of mind of affected customers. This form of fraud occurs when unauthorized individuals gain access to users’ accounts and exploit them for fraudulent activities, leading to substantial financial losses and significant disruptions. In this article, we delve into the key indicators of ATO and provide insights into strategies FIs can employ to identify and prevent such fraudulent activities effectively.
Understanding Account Takeover Fraud
ATO involves fraudulent access to a customer’s financial account, enabling perpetrators to carry out unauthorized transactions, modify account details, or siphon funds unlawfully. Fraudsters employ various tactics, including phishing scams, social engineering, or exploiting security vulnerabilities within FIs’ systems, to gain illicit access. Once inside, they perpetrate activities that inflict financial losses on both FIs and their customers.
The Risks Associated with ATO
The ramifications of ATO extend beyond mere financial losses, encompassing reputational damage, legal penalties, identity theft, and operational disruptions. These risks underscore the urgency for FIs to fortify their security measures and safeguard against the perils of account takeover fraud.
Methods Employed by Fraudsters
Fraudsters employ a spectrum of methods to execute ATO, including:
1. Phishing: Sending deceptive emails or messages impersonating FIs to coax customers into divulging their login credentials on counterfeit websites.
2. Social Engineering: Manipulating customers into revealing their login credentials through psychological manipulation, often by posing as bank representatives.
3. Malware: Infecting customers’ devices with malware to capture login credentials entered on banking websites.
4. SIM Swapping: Hijacking customers’ mobile numbers to gain access to their accounts, typically by coercing telecom operators to transfer numbers to SIM cards under their control.
5. Password Guessing: Employing automated tools to guess usernames and passwords based on information obtained through phishing or social engineering.
Identifying ATO necessitates vigilance for certain telltale signs:
1. Unusual Login Patterns: Anomalies such as logins from unfamiliar locations, devices, or odd hours may indicate unauthorized account access.
2. Sudden Changes in Account Information: Abrupt alterations in personal information like email addresses, mailing addresses, or phone numbers suggest potential account takeover attempts.
3. Unfamiliar Transactions: Spikes in transactions, particularly involving large amounts or international transfers, signal unauthorized account activity.
4. Multiple Failed Login Attempts: Excessive unsuccessful login attempts hint at illicit efforts to gain access using stolen credentials or brute force attacks.
5. Unusual Account Activity: Abrupt deviations from typical transaction patterns indicate potential account compromise by fraudsters.
To mitigate the risks posed by ATO, FIs can adopt the following proactive measures:
1. Implement Robust Security Measures: Employ multi-factor authentication and advanced security protocols like one-time passwords (OTPs) and biometrics to fortify account security.
2. Educate Customers: Regularly educate customers on ATO risks and guide them on adopting strong password practices and exercising caution while sharing personal information online.
3. Monitor Accounts for Suspicious Activity: Continuously monitor accounts for signs of ATO, promptly notifying customers of any detected anomalies and taking swift action to secure compromised accounts.
4. Utilize Advanced Fraud Detection Tools: Leverage artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning algorithms to detect patterns indicative of ATO, complemented by continuous control monitoring and fraud prevention solutions.
5. Collaborate With Other Institutions: Foster collaboration among FIs to share insights on emerging ATO threats and best practices for prevention, enhancing the collective resilience of the financial industry.
6. Combining ATO Prevention with AML Compliance
Integrating data and strategies from anti-money laundering (AML) compliance programs with fraud prevention efforts can bolster ATO detection and mitigation. By leveraging insights gleaned from transaction monitoring, identity verification, and KYC processes, FIs can enhance their capacity to combat various forms of fraud, including ATO.
Conclusion
Account takeover fraud poses a formidable challenge to FIs and their customers, necessitating robust preventive measures and vigilant oversight. By heeding the signs of ATO, implementing stringent security protocols, and leveraging advanced fraud detection solutions, FIs can fortify their defenses and mitigate the impact of fraudulent activities. To explore how Ahrvo Comply’s comprehensive fraud detection and prevention solutions can bolster ATO prevention and enhance AML compliance, reach out to us today.